- UID
- 10108
- 积分
- 5956
- 精华
- 贡献
-
- 威望
-
- 活跃度
-
- D豆
-
- 在线时间
- 小时
- 注册时间
- 2002-9-17
- 最后登录
- 1970-1-1
|
马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能,让你轻松玩转社区。
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册

×
http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/22568/Computational-Geometry-C-and-WykobiComputational Geometry, C++ and WykobiA brief introduction in computational geometry algorithms using Wykobi and C++
Introduction Good C++ computational geometry libraries to date have been hideously over-designed and incorporate usage patterns that in most cases require extensive redesigns and rewrites of code in order to functionally integrate within an existing project.
Sometimes a lightweight portable solution that has a bit of error is deemed to be more appropriate and reasonable. However these libraries even though being more than able to cater for such a requirement still burden the end user with undue code clutter, very steep learning curves and in some cases unnecessary overheads.
The solution to such a situation is to simplify use, implementation and application. This can be achieved by reducing the number of contact points between the computational geometry back-end and the developer-application combo. But at the same time giving full control of the computations and ensuing folding processes to the user to the extent where the user can decide between using a general solution for a particular problem or a more specialized solution.
For example, say you have two line segments and you want to know if they are intersecting, one could use a general solution, but say if you had prior knowledge that the line segments were either always going to be vertical or horizontal, this would allow one to use a more efficient method to obtain the same result. Typically (but not always) a generalized result is less efficient than a specialised result for the specialised case - by virtue of the fact that the generalised result has to take into account the 1001 other possible scenarios.
A possible solution to the above mentioned problem is Wykobi. Wykobi is an efficient, robust and simple to use multi-platform 2D/3D computational geometry library. Wykobi provides a concise, predictable, and deterministic interface for geometric primitives and complex geometric routines using and conforming to the ISO/IEC 14882:2003 C++ language specification.
The design and structure of Wykobi lends itself to easy and seamless integration into projects of any scale that require a robust yet efficient 2D/3D computational geometry back-end.
Wykobi as a library can be used to efficiently and seamlessly solve complex geometric problems such as collision and proximity detection, efficient spatial queries and geometric constructions used in areas as diverse as gaming, computer aided design and manufacture, electronic design and geographic information systems - just to name a few.
Wykobi provides a series of primitive geometric structures for use within the various algorithms of interest such as intersections, distances, inclusions and clipping operations.
The Wykobi Data StructuresThe Point Type Basic point types, which are zero dimensional entities that exist in either 2D, 3D or n-dimensions.
template<typename T = Float>class point2d : public geometric_entity {};template<typename T = Float>class point3d : public geometric_entity {};template<typename T = Float, std::size_t Dimension>class pointnd : public geometric_entity {};
The Line Type Line type, which is a 1 dimensional entity of infinite length that is described by two points within its present dimension.
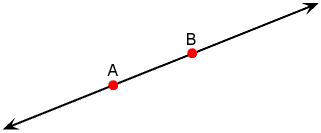
template <typename T, unsigned int Dimension>class line : public geometric_entity {};
The Segment (Line-Segment) Type Segment type, similar to the line type, but is of finite length bounded by the two points which describe it within its present dimension.
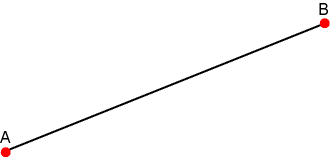
template <typename T, unsigned int Dimension>class segment : public geometric_entity {};
The Ray Type Ray type, A directed half-infinite line or half-line. A ray has an origin point and a vector that describes the direction in which all the points that are members of the set of points that make up the ray exist upon.
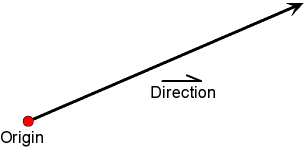
template <typename T, unsigned int Dimension>class ray : public geometric_entity {};
The Triangle Type Triangle type, A geometric primitive that is comprised of 3 unique points, which produce 3 unique edges.
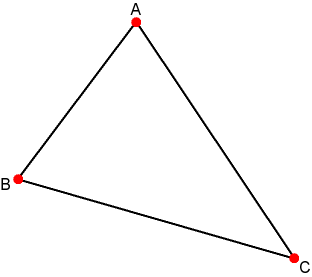
template <typename T, unsigned int Dimension>class triangle : public geometric_entity {};
The Rectangle Type Rectangle type, An axis aligned 4 sided geometric primitive, described by two bounding points in 2D. A rectangle's form in 3D and higher dimensions is a box.
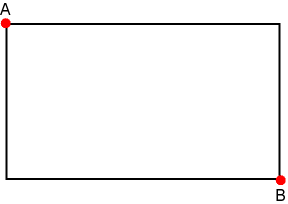
template<typename T>class rectangle : public geometric_entity {};
|
|
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 |申请友链|Archiver|手机版|小黑屋|辽公网安备|晓东CAD家园
( 辽ICP备15016793号 )
|申请友链|Archiver|手机版|小黑屋|辽公网安备|晓东CAD家园
( 辽ICP备15016793号 )