马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能,让你轻松玩转社区。
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册

×
本帖最后由 newer 于 2016-10-25 17:52 编辑
贴篇文献吧,欢迎大家讨论!!
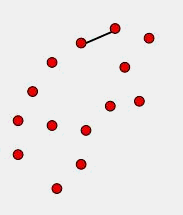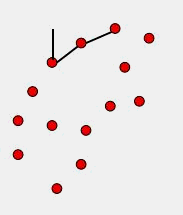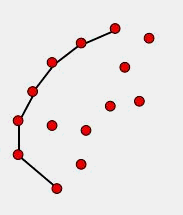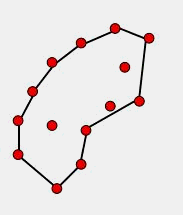
近期遇到一个计算几何问题,需要从点集中重建一个合理的几何形状。这个问题既有二维的也有三维的,二维的情况相对简单一点,即给出平面区域的一系列散点,求出一定程度上反映这些散点轮廓的平面多边形,给出边的连接方式即可。如从下图的左图散点重建为右图的形状:
不过这里有一些细节需要注意,必须明确这一系列点的含义,有时给出的点集是表征图形边界的,如左图的情况;有时则是表征图形所覆盖的范围,即在图形的内部也有一定的点分布。这两种不同的含义是和具体的应用场景相关的。 | | 有的场景 是求散点描绘的轮廓 | 有的场景是求散点分布区域的边界轮廓 |
凹包与Alpha shape
有不少计算几何领域的资料探讨过这一类问题的解决方案,笔者也曾经阅读过部分相关的文献,也在网络上进行过一些搜索。本文不能一一去介绍所有的方法,所以就介绍几种简单直观的方法来解决二维点集重建平面多边形的问题。 首先很多学计算机的人都知道 凸包 ,凸包求取的是覆盖所有点的凸多边形,由于限定死了一定要凸多边形,所以凸包不是本文所讨论问题的解决方案。本文所求的形状肯定不能否定存在凹陷的部分,因而可以联想到这个问题的解是否是求一种“凹包”,或者说一种广义的参数化的凸包。事实上的确有凹包的概念,英文叫做 concave hull(凸包叫convex hull)。不过于凸包的情况不同,凹包没有特别明确的定义,给定一个较不规则的点集,可以有各种各样的凹包,但凸包是确定的,如下图所示。
进一步查找相关的资料可以发现一个叫做 alpha shape 的概念。这个概念最早出现于论文 "On the shape of a set of points in the plane" 中。alpha shape有较为正式的定义,若要简单点解释它,alpha shape其实就是在凸包基础上多了一个可以设定的参数α,因为这个α,在alpha shape重建形状的过程中可能就不会像凸包一样连接相距过远的顶点。参数α若趋于无穷大,则这个alpha shape会无无限接近凸包;而α取小了,则alpha shape会倾向于在一定位置凹陷进去,以更加贴合点集的外形。选择合理的α就能够控制生成的形状让其更加符合点集所描绘的形状。 所以给出一个α值,就有点类似于给出一个长度的限制,例如让多边形的任何一边长度不超过R。 为了更好的展示和测试程序,笔者特地开发了一个基于WPF技术的小软件ConcaveGenerator用来展示算法效果,下文展示的很多图都是对这个软件截图的。如有兴趣可以在这里下载。
第一种思路--基于Delaunay三角化
有一定计算几何基础的人一定熟悉 Delaunay三角化 ,通过这一个过程可以形成Delaunay三角网,假如我们为想要求取形状的点集上使用Delaunay三角化算法,可以得到如下的三角网。
一看到这样的三角网,就不难想到一个好点子:因为我们想要求取的形状就是Delaunay三角网的子集,所以我们只需要从Delaunay三角网的最外层边开始外不断的删去超过长度限制的边,当这个过程结束时,我们就能够得到一个大致符合我们预期的形状。
| | 点集的Delaunay三角网 | 删掉边上太长的边就能形成预期的形状 |
所以总结这个思路,输入为点集S和长度限制R的求取凹包的边列表算法的过程如下: - 为点集S求取Delaunay三角网M,三角网用标准Mesh形式表示。
- 为M初始化所有Edge对象,并求取Edge的长度以及邻接三角形集合。其中邻接2个三角形的边为内部边,1个三角形的为边界边,0个三角形的为计算过程中会退化的边。
- 将所有长度大于R的边界边加入队列,并当队列非空时循环下列过程:
- 从队列中取出一条边E,得到E的唯一邻接三角形T。
- 找到T中另外两个边E1,E2将他们的邻接三角形集合删去T。
- 将E1,E2中新形成的长度大于R的边界边加入队列。
- 将E置无效标记,若E1,E2有退化的,也置无效标记。
- 收集所有有效的边界边,形成边列表,输出。
以下ConcaveGenerator是在这部分的代码,其中Delaunay三角化的实现有比较多的代码能参考,这里是使用了Stackoverflow上一个snippet:
public class DelaunayTriangulation
{
public const int MaxVertices = 500;
public const int MaxTriangles = 1000;
public dVertex[] Vertex = new dVertex[MaxVertices];
public dTriangle[] Triangle = new dTriangle[MaxTriangles];
private bool InCircle(long xp, long yp, long x1, long y1, long x2, long y2, long x3, long y3, double xc, double yc, double r)
{
double eps;
double m1;
double m2;
double mx1;
double mx2;
double my1;
double my2;
double dx;
double dy;
double rsqr;
double drsqr;
eps = 0.000000001;
if (Math.Abs(y1 - y2) < eps && Math.Abs(y2 - y3) < eps)
{
return false;
}
if (Math.Abs(y2 - y1) < eps)
{
m2 = (-(Convert.ToDouble(x3) - Convert.ToDouble(x2)) / (Convert.ToDouble(y3) - Convert.ToDouble(y2)));
mx2 = Convert.ToDouble((x2 + x3) / 2.0);
my2 = Convert.ToDouble((y2 + y3) / 2.0);
xc = Convert.ToDouble((x2 + x1) / 2.0);
yc = Convert.ToDouble(m2 * (xc - mx2) + my2);
}
else if (Math.Abs(y3 - y2) < eps)
{
m1 = (-(Convert.ToDouble(x2) - Convert.ToDouble(x1)) / (Convert.ToDouble(y2) - Convert.ToDouble(y1)));
mx1 = Convert.ToDouble((x1 + x2) / 2.0);
my1 = Convert.ToDouble((y1 + y2) / 2.0);
xc = Convert.ToDouble((x3 + x2) / 2.0);
yc = Convert.ToDouble(m1 * (xc - mx1) + my1);
}
else
{
m1 = (-(Convert.ToDouble(x2) - Convert.ToDouble(x1)) / (Convert.ToDouble(y2) - Convert.ToDouble(y1)));
m2 = (-(Convert.ToDouble(x3) - Convert.ToDouble(x2)) / (Convert.ToDouble(y3) - Convert.ToDouble(y2)));
mx1 = Convert.ToDouble((x1 + x2) / 2.0);
mx2 = Convert.ToDouble((x2 + x3) / 2.0);
my1 = Convert.ToDouble((y1 + y2) / 2.0);
my2 = Convert.ToDouble((y2 + y3) / 2.0);
xc = Convert.ToDouble((m1 * mx1 - m2 * mx2 + my2 - my1) / (m1 - m2));
yc = Convert.ToDouble(m1 * (xc - mx1) + my1);
}
dx = (Convert.ToDouble(x2) - Convert.ToDouble(xc));
dy = (Convert.ToDouble(y2) - Convert.ToDouble(yc));
rsqr = Convert.ToDouble(dx * dx + dy * dy);
r = Convert.ToDouble(Math.Sqrt(rsqr));
dx = Convert.ToDouble(xp - xc);
dy = Convert.ToDouble(yp - yc);
drsqr = Convert.ToDouble(dx * dx + dy * dy);
if (drsqr <= rsqr)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
private int WhichSide(long xp, long yp, long x1, long y1, long x2, long y2)
{
double equation;
equation = ((Convert.ToDouble(yp) - Convert.ToDouble(y1)) * (Convert.ToDouble(x2) - Convert.ToDouble(x1))) - ((Convert.ToDouble(y2) - Convert.ToDouble(y1)) * (Convert.ToDouble(xp) - Convert.ToDouble(x1)));
if (equation > 0)
{
return -1;
//WhichSide = -1;
}
else if (equation == 0)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return 1;
}
}
public int Triangulate(int nvert)
{
bool[] Complete = new bool[MaxTriangles];
long[,] Edges = new long[3, MaxTriangles * 3 + 1];
long Nedge;
long xmin;
long xmax;
long ymin;
long ymax;
long xmid;
long ymid;
double dx;
double dy;
double dmax;
int i;
int j;
int k;
int ntri;
double xc = 0.0;
double yc = 0.0;
double r = 0.0;
bool inc;
xmin = Vertex[1].x;
ymin = Vertex[1].y;
xmax = xmin;
ymax = ymin;
for (i = 2; i <= nvert; i++)
{
if (Vertex[i].x < xmin)
{
xmin = Vertex[i].x;
}
if (Vertex[i].x > xmax)
{
xmax = Vertex[i].x;
}
if (Vertex[i].y < ymin)
{
ymin = Vertex[i].y;
}
if (Vertex[i].y > ymax)
{
ymax = Vertex[i].y;
}
}
dx = Convert.ToDouble(xmax) - Convert.ToDouble(xmin);
dy = Convert.ToDouble(ymax) - Convert.ToDouble(ymin);
if (dx > dy)
{
dmax = dx;
}
else
{
dmax = dy;
}
xmid = (xmax + xmin) / 2;
ymid = (ymax + ymin) / 2;
Vertex[nvert + 1].x = Convert.ToInt64(xmid - 2 * dmax);
Vertex[nvert + 1].y = Convert.ToInt64(ymid - dmax);
Vertex[nvert + 2].x = xmid;
Vertex[nvert + 2].y = Convert.ToInt64(ymid + 2 * dmax);
Vertex[nvert + 3].x = Convert.ToInt64(xmid + 2 * dmax);
Vertex[nvert + 3].y = Convert.ToInt64(ymid - dmax);
Triangle[1].vv0 = nvert + 1;
Triangle[1].vv1 = nvert + 2;
Triangle[1].vv2 = nvert + 3;
Complete[1] = false;
ntri = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= nvert; i++)
{
Nedge = 0;
j = 0;
do
{
j = j + 1;
if (Complete[j] != true)
{
inc = InCircle(Vertex[i].x, Vertex[i].y, Vertex[Triangle[j].vv0].x, Vertex[Triangle[j].vv0].y, Vertex[Triangle[j].vv1].x, Vertex[Triangle[j].vv1].y, Vertex[Triangle[j].vv2].x, Vertex[Triangle[j].vv2].y, xc, yc, r);
if (inc)
{
Edges[1, Nedge + 1] = Triangle[j].vv0;
Edges[2, Nedge + 1] = Triangle[j].vv1;
Edges[1, Nedge + 2] = Triangle[j].vv1;
Edges[2, Nedge + 2] = Triangle[j].vv2;
Edges[1, Nedge + 3] = Triangle[j].vv2;
Edges[2, Nedge + 3] = Triangle[j].vv0;
Nedge = Nedge + 3;
Triangle[j].vv0 = Triangle[ntri].vv0;
Triangle[j].vv1 = Triangle[ntri].vv1;
Triangle[j].vv2 = Triangle[ntri].vv2;
Complete[j] = Complete[ntri];
j = j - 1;
ntri = ntri - 1;
}
}
}
while (j < ntri);
for (j = 1; j <= Nedge - 1; j++)
{
if (Edges[1, j] != 0 && Edges[2, j] != 0)
{
for (k = j + 1; k <= Nedge; k++)
{
if (Edges[1, k] != 0 && Edges[2, k] != 0)
{
if (Edges[1, j] == Edges[2, k])
{
if (Edges[2, j] == Edges[1, k])
{
Edges[1, j] = 0;
Edges[2, j] = 0;
Edges[1, k] = 0;
Edges[2, k] = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
for (j = 1; j <= Nedge; j++)
{
if (Edges[1, j] != 0 && Edges[2, j] != 0)
{
ntri = ntri + 1;
Triangle[ntri].vv0 = Edges[1, j];
Triangle[ntri].vv1 = Edges[2, j];
Triangle[ntri].vv2 = i;
Complete[ntri] = false;
}
}
}
i = 0;
do
{
i = i + 1;
if (Triangle[i].vv0 > nvert || Triangle[i].vv1 > nvert || Triangle[i].vv2 > nvert)
{
Triangle[i].vv0 = Triangle[ntri].vv0;
Triangle[i].vv1 = Triangle[ntri].vv1;
Triangle[i].vv2 = Triangle[ntri].vv2;
i = i - 1;
ntri = ntri - 1;
}
}
while (i < ntri);
return ntri;
}
public static double Diameter(double Ax, double Ay, double Bx, double By, double Cx, double Cy)
{
double x, y;
double a = Ax;
double b = Bx;
double c = Cx;
double m = Ay;
double n = By;
double k = Cy;
double A = a * b * b + a * n * n + a * a * c - b * b * c + m * m * c - n * n * c - a * c * c - a * k * k - a * a * b + b * c * c - m * m * b + b * k * k;
double B = a * n + m * c + k * b - n * c - a * k - b * m;
y = A / B / 2;
double AA = b * b * m + m * n * n + a * a * k - b * b * k + m * m * k - n * n * k - c * c * m - m * k * k - a * a * n + c * c * n - m * m * n + k * k * n;
double BB = b * m + a * k + c * n - b * k - c * m - a * n;
x = AA / BB / 2;
return Math.Sqrt((Ax - x) * (Ax - x) + (Ay - y) * (Ay - y));
}
public static double MaxEdge(double Ax, double Ay, double Bx, double By, double Cx, double Cy)
{
double len1 = Math.Sqrt((Ax - Bx) * (Ax - Bx) + (Ay - By) * (Ay - By));
double len2 = Math.Sqrt((Cx - Bx) * (Cx - Bx) + (Cy - By) * (Cy - By));
double len3 = Math.Sqrt((Ax - Cx) * (Ax - Cx) + (Ay - Cy) * (Ay - Cy));
double len = len1 > len2 ? len1 : len2;
return len > len3 ? len : len3;
}
}
以下是基于Delaunay的求凹包算法部分核心函数:
public struct dVertex
{
public long x;
public long y;
public long z;
}
public struct dTriangle
{
public long vv0;
public long vv1;
public long vv2;
}
public struct OrTriangle
{
public Point2d p0;
public Point2d p1;
public Point2d p2;
}
public struct Triangle
{
public int P0Index;
public int P1Index;
public int P2Index;
public int Index;
public Triangle(int p0index, int p1index, int p2index)
{
this.P0Index = p0index;
this.P1Index = p1index;
this.P2Index = p2index;
this.Index = -1;
}
public Triangle(int p0index, int p1index, int p2index, int index)
{
this.P0Index = p0index;
this.P1Index = p1index;
this.P2Index = p2index;
this.Index = index;
}
}
public struct EdgeInfo
{
public int P0Index;
public int P1Index;
public List<int> AdjTriangle;
public bool Flag;
public double Length;
public int GetEdgeType()
{
return AdjTriangle.Count;
}
public bool IsValid()
{
return P0Index != -1;
}
public EdgeInfo(int d)
{
P0Index = -1;
P1Index = -1;
Flag = false;
AdjTriangle = new List<int>();
Length = -1;
}
}
public class DelaunayMesh2d
{
public List<Point2d> Points;
public List<Triangle> Faces;
public EdgeInfo[,] Edges;
public DelaunayMesh2d()
{
Points = new List<Point2d>();
Faces = new List<Triangle>();
}
public int AddVertex(Point2d p)
{
Points.Add(p);
return Points.Count - 1;
}
public int AddFace(Triangle t)
{
Faces.Add(t);
return Faces.Count - 1;
}
public void InitEdgesInfo()
{
Edges = new EdgeInfo[Points.Count, Points.Count];
for (int i = 0; i < Points.Count; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Points.Count; j++)
{
Edges[i, j] = new EdgeInfo(0);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < Faces.Count; i++)
{
Triangle t = Faces[i];
SetEdge(t, i);
}
}
private void SetEdge(Triangle t, int i)
{
if (t.P0Index < t.P1Index)
{
Edges[t.P0Index, t.P1Index].P0Index = t.P0Index;
Edges[t.P0Index, t.P1Index].P1Index = t.P1Index;
Edges[t.P0Index, t.P1Index].AdjTriangle.Add(i);
Edges[t.P0Index, t.P1Index].Length = BallConcave.GetDistance(Points[t.P0Index], Points[t.P1Index]);
}
else
{
Edges[t.P1Index, t.P0Index].P0Index = t.P1Index;
Edges[t.P1Index, t.P0Index].P1Index = t.P0Index;
Edges[t.P1Index, t.P0Index].AdjTriangle.Add(i);
Edges[t.P1Index, t.P0Index].Length = BallConcave.GetDistance(Points[t.P0Index], Points[t.P1Index]);
}
if (t.P1Index < t.P2Index)
{
Edges[t.P1Index, t.P2Index].P0Index = t.P1Index;
Edges[t.P1Index, t.P2Index].P1Index = t.P2Index;
Edges[t.P1Index, t.P2Index].AdjTriangle.Add(i);
Edges[t.P1Index, t.P2Index].Length = BallConcave.GetDistance(Points[t.P1Index], Points[t.P2Index]);
}
else
{
Edges[t.P2Index, t.P1Index].P0Index = t.P2Index;
Edges[t.P2Index, t.P1Index].P1Index = t.P1Index;
Edges[t.P2Index, t.P1Index].AdjTriangle.Add(i);
Edges[t.P2Index, t.P1Index].Length = BallConcave.GetDistance(Points[t.P1Index], Points[t.P2Index]);
}
if (t.P0Index < t.P2Index)
{
Edges[t.P0Index, t.P2Index].P0Index = t.P0Index;
Edges[t.P0Index, t.P2Index].P1Index = t.P2Index;
Edges[t.P0Index, t.P2Index].AdjTriangle.Add(i);
Edges[t.P0Index, t.P2Index].Length = BallConcave.GetDistance(Points[t.P0Index], Points[t.P2Index]);
}
else
{
Edges[t.P2Index, t.P0Index].P0Index = t.P2Index;
Edges[t.P2Index, t.P0Index].P1Index = t.P0Index;
Edges[t.P2Index, t.P0Index].AdjTriangle.Add(i);
Edges[t.P2Index, t.P0Index].Length = BallConcave.GetDistance(Points[t.P0Index], Points[t.P2Index]);
}
}
public void ExecuteEdgeDecimation(double length)
{
Queue<EdgeInfo> queue = new Queue<EdgeInfo>();
for (int i = 0; i < Points.Count; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Points.Count; j++)
{
if (i < j && Edges[i, j].IsValid())
{
if (Edges[i, j].GetEdgeType() == 0)
{
throw new Exception();
}
if (Edges[i, j].Length > length && Edges[i, j].GetEdgeType() == 1)
{
queue.Enqueue(Edges[i, j]);
}
}
}
}
EdgeInfo[] opp1Temp = new EdgeInfo[2];
while (queue.Count != 0)
{
EdgeInfo info = queue.Dequeue();
if (info.AdjTriangle.Count != 1)
throw new Exception();
int tindex = info.AdjTriangle[0];
Triangle t = Faces[tindex];
InitOppEdge(opp1Temp, t, info);
SetInvalid(info.P0Index, info.P1Index);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
EdgeInfo e = opp1Temp[i];
e.AdjTriangle.Remove(tindex);
if (e.GetEdgeType() == 0)
{
SetInvalid(e.P0Index, e.P1Index);
}
else if (e.GetEdgeType() == 1 && e.Length > length)
{
queue.Enqueue(e);
}
}
}
}
public List<EdgeInfo> GetBoundaryEdges()
{
List<EdgeInfo> list = new List<EdgeInfo>();
for (int i = 0; i < Points.Count; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Points.Count; j++)
{
if (i < j)
{
if (Edges[i, j].GetEdgeType() == 1)
{
list.Add(Edges[i, j]);
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
private void SetInvalid(int i, int j)
{
Edges[i, j].AdjTriangle.Clear();
Edges[i, j].Flag = true;
Edges[i, j].P0Index = -1;
Edges[i, j].P1Index = -1;
}
private void InitOppEdge(EdgeInfo[] opp1Temp, Triangle t, EdgeInfo info)
{
int vindex = t.P0Index + t.P1Index + t.P2Index - info.P0Index - info.P1Index;
if (vindex < info.P0Index)
{
opp1Temp[0] = Edges[vindex, info.P0Index];
}
else
{
opp1Temp[0] = Edges[info.P0Index, vindex];
}
if (vindex < info.P1Index)
{
opp1Temp[1] = Edges[vindex, info.P1Index];
}
else
{
opp1Temp[1] = Edges[info.P1Index, vindex];
}
}
}
下图是用基于Delauney的方法生成的凹包,看上去大致符合我们的预期:
第二种思路--滚边法(Edge Pivoting)
这是笔者最初想到的一个从求凸包的 Graham Scan 算法衍生出来的一个方法。求凸包的Graham Scan算法先找到一个Y最低的点作为起始点,然后使用叉积角度判断的方法去判断点的走向,最后在栈内留下了凸包的点序列。具体的算法讲解与代码,网上一搜各种有,这里就不详细表述。本文要介绍的方法也是和Graham Scan法从同一个出发点出发,通过扫描角度来确定下一个点。具体算法流程从下面的图文说明可以大致看出来:
首先要实现这个算法,需要对随机的一个点查询距离其几何距离在R内的所有点,即求所谓的 R邻域 。这个R 邻域 算法是 KNN (K-nearest neighbors)算法的一个变形,可以在小于O(n 2 )的复杂度下求取R领域,本文为了简单起见没有实现这个基于K-d Tree 的算法,感兴趣的读者可以查阅相关资料了解这个算法。本文涉及的应用场景因为点数目不大,所以使用的方法没有过多考虑效率,实现R邻域的方式是先建立一个n*n的二维数组存储所有点两两之间的距离,然后遍历一次二维数组,为所有的点建立一个R邻域列表,该列表中存储了对应点R邻域的索引值,这个列表很有用,下面要介绍的滚球法也利用了这个列表。 实际上不难理解,假设AB为凹包的一个边,那么其下一个点C必然是在B的R邻域点中选择。我们实现这个算法的关键,就是为AB边找一个合适的C点。这里笔者设想的寻找C的方法使用如下原则: - 假如B的R领域除了A就只有一个点,那么那个点就是C。
- 以B为圆心从向量BA出发转圈扫描,遇到的第一个点为C。
这里涉及到一个小算法,即所谓的极坐标方向排序问题,这个问题的描述是:给定一个原点P和一个初始方向n,如何为平面上的点集S排序,使得点集中的点P1,P2...PN与P的连接是按从n开始的逆时针排列的。这个问题搜一搜stackoverflow即得到一个很好的解答,这个 链接 里一个人给出一个用于比较的函数,一旦有了比较函数,排序也不成问题,这个比较函数在后面的方法中会出现。其具体的比较原理如果对向量的点积叉积有所了解也不难理解。这里不妨提一下点集叉积的结果符号的几何含义: - 向量a与b的点集结果为一个实数,计算方式是ax*bx+ay*by,满足交换率,为正值代表ab夹角小于90度,为锐角,负值代表夹角大于90度(谈夹角的话是指0-180度范围),为钝角。
- 向量a与b的叉积结果为一个向量,其数值的计算方法是ax*bx-ay*by,不满足交换率,为正值代表向量b处于向量a的逆时针方向(即a逆时针转一个小于180的角能转到b),负值代表向量b处于向量a的顺时针方向(即a顺时针转一个小于180的角能转到b,非要逆时针转则必然超过180度)。
那么找C点的第二条实现的方式就类似于对一个数组找最小值那样,通过比较找到最小的角度,这个有最小角偏向的就是C点。 不过遗憾的是这个思路其实是问题的,测试表明对一些点集采用这个方法会有BUG出现。例如当C点出现在BA向量小于90度的方向时,形成的BC边和AB边具有大致相反的方向,会导致下一步的寻点出现逆向,故这个思路不算是一个成功的思路,不过失败是成功之母,它却引出另一个滚球法的思路,相比这个思路具有更好的鲁棒性。
第三种思路--滚球法(Ball Pivoting)
对于任何点集,我们把这些点想象为钉在平面上的钉子。假如拿一个半径大于一定值的球去从边界接近这个钉群,我们可以用这个球在这些钉子群的边界滚一圈,每次滚动,球都能接触到两个钉子而被卡住。 这个思路要求一个合法的R,R太小就没法形成一个闭合的图形。由于我们讨论问题的初衷是要形成一个合适的多边形而不是0个或多个,这样对R的选择就应该有一个限制,太小的R必然出不了结果,这里姑且假设给的R值是合适的。此过程若形成一个多边形,则多变形的最长的边一定小于球的直径。所以算法输入参数为R,意味着拿一个半径为R/2的圆去滚。如下图显示了这个滚球的过程:
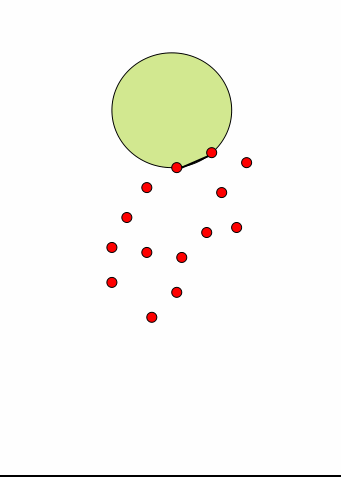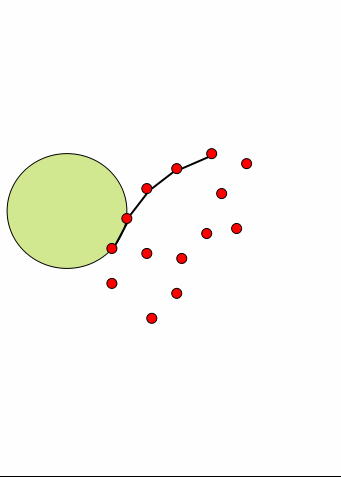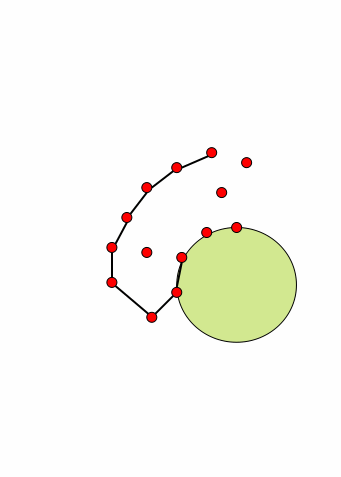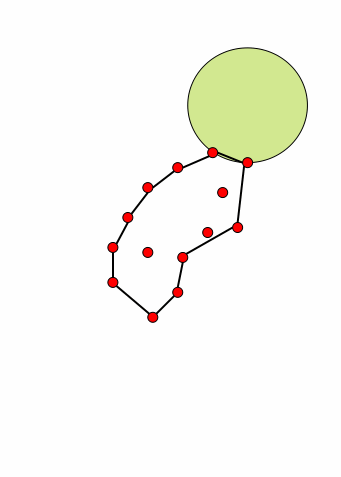
我们不难发现一个性质,对于任何一次翻滚,假设从弦DE翻转到新弦EF,圆不可能扫过任何的其他点,因为假如扫到其他点,必然会被这个点所卡住,那么新弦就不可能是EF了。这样我们只需对极坐标排序后的E点的R邻域依次寻找符合不覆盖其他点的圆即可。 | | 圆在翻滚时候不能扫到其他点 | 对E的R邻域测试圆覆盖情况寻找合适的F |
这个算法的执行过程和滚边法相似,算法结构都是先找起始点,然后循环寻找下一个点,核心问题也是从边DE线段出发找新线段EF,只是不再使用边去扫,而是用圆去扫。这里先给出这个算法的大致步骤: - 先像求凸包那样求出一个Y值最小(Y值相同则取X最大)的点,作为初始点A,此点一定在凹包上。
- 从此点出发,(1,0)为基准向量,先找一个小于R的边作为初始边,这时这个点即为B,此时一个半径为R/2的圆就卡在了AB上,此时第一个弦AB就找到了。
- 循环寻找接下来的弦,假如上一条弦为DE,则下一条弦必然从E开始,连接到E的一个R领域内的点F。寻找F可以使用如下的原则:先对E的R领域的点,以E为中心ED向量为基准进行极坐标方向排序,之后依次为R领域点F0~FN建立以EFi为弦的圆,然后检查其中是否包含其他F0~FN的点,若不存在,则EFi即为新弦,则跳出循环。
- 依次找到所有的弦,直到找不到新弦或遇到以前已经作为弦的点为止。
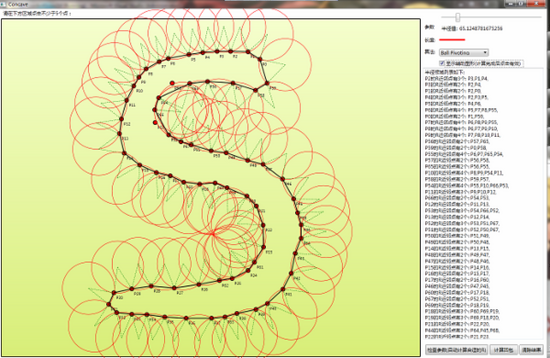
一旦R值给的比较好,这个过程一定能给出一个闭合的图形。下图为几张用ConcaveGenerator生成的图片示例,其中检查参数按钮会自动给一个能让所有点都有至少2个领域的R值。
上述过程其实感觉还有很大的优化余地,不过在点数不是很多的场合还是能姑且一用的。
在ConcaveGenerator中这部分的代码为下面的C#类,这个类既实现了滚边法也实现了滚球法:
public class BallConcave
{
public MainWindow main;
struct Point2dInfo : IComparable<Point2dInfo>
{
public Point2d Point;
public int Index;
public double DistanceTo;
public Point2dInfo(Point2d p,int i,double dis)
{
this.Point = p;
this.Index = i;
this.DistanceTo = dis;
}
public int CompareTo(Point2dInfo other)
{
return DistanceTo.CompareTo(other.DistanceTo);
}
public override string ToString()
{
return Point+","+Index+","+DistanceTo;
}
}
public BallConcave(List<Point2d> list)
{
this.points = list;
points.Sort();
flags = new bool[points.Count];
for (int i = 0; i < flags.Length; i++)
flags[i] = false;
InitDistanceMap();
InitNearestList();
}
private bool[] flags;
private List<Point2d> points;
private double[,] distanceMap;
private List<int>[] rNeigbourList;
private void InitNearestList()
{
rNeigbourList = new List<int>[points.Count];
for (int i = 0; i < rNeigbourList.Length; i++)
{
rNeigbourList[i] = GetSortedNeighbours(i);
}
}
private void InitDistanceMap()
{
distanceMap = new double[points.Count, points.Count];
for (int i = 0; i < points.Count; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < points.Count; j++)
{
distanceMap[i, j] = GetDistance(points[i], points[j]);
}
}
}
public double GetRecomandedR()
{
double r=double.MinValue;
for (int i = 0; i < points.Count; i++)
{
if (distanceMap[i, rNeigbourList[i][1]] > r)
r = distanceMap[i, rNeigbourList[i][1]];
}
return r;
}
public double GetMinEdgeLength()
{
double min = double.MaxValue;
for (int i = 0; i < points.Count; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < points.Count; j++)
{
if (i < j)
{
if (distanceMap[i, j] < min)
min = distanceMap[i, j];
}
}
}
return min;
}
public List<Point2d> GetConcave_Ball(double radius)
{
List<Point2d> ret = new List<Point2d>();
List<int>[] adjs = GetInRNeighbourList(2*radius);
ret.Add(points[0]);
//flags[0] = true;
int i = 0, j = -1, prev = -1;
while (true)
{
j = GetNextPoint_BallPivoting(prev, i, adjs[i],radius);
if (j == -1)
break;
Point2d p = BallConcave.GetCircleCenter(points[i], points[j], radius);
ret.Add(points[j]);
flags[j] = true;
prev = i;
i = j;
}
return ret;
}
public List<Point2d> GetConcave_Edge(double radius)
{
List<Point2d> ret = new List<Point2d>();
List<int>[] adjs = GetInRNeighbourList(2 * radius);
ret.Add(points[0]);
int i = 0, j = -1, prev = -1;
while (true)
{
j = GetNextPoint_EdgePivoting(prev, i, adjs[i], radius);
if (j == -1)
break;
//Point2d p = BallConcave.GetCircleCenter(points[i], points[j], radius);
ret.Add(points[j]);
flags[j] = true;
prev = i;
i = j;
}
return ret;
}
private bool CheckValid(List<int>[] adjs)
{
for (int i = 0; i < adjs.Length; i++)
{
if (adjs[i].Count < 2)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public bool CompareAngel(Point2d a, Point2d b, Point2d m_origin, Point2d m_dreference)
{
Point2d da = new Point2d(a.X - m_origin.X, a.Y - m_origin.Y);
Point2d db = new Point2d(b.X - m_origin.X, b.Y - m_origin.Y);
double detb = GetCross(m_dreference, db);
// nothing is less than zero degrees
if (detb == 0 && db.X * m_dreference.X + db.Y * m_dreference.Y >= 0) return false;
double deta = GetCross(m_dreference, da);
// zero degrees is less than anything else
if (deta == 0 && da.X * m_dreference.X + da.Y * m_dreference.Y >= 0) return true;
if (deta * detb >= 0) {
// both on same side of reference, compare to each other
return GetCross(da, db) > 0;
}
// vectors "less than" zero degrees are actually large, near 2 pi
return deta > 0;
}
public int GetNextPoint_EdgePivoting(int prev,int current,List<int> list,double radius)
{
if (list.Count == 2 && prev != -1)
{
return list[0] + list[1] - prev;
}
Point2d dp;
if (prev == -1)
dp = new Point2d(1, 0);
else
dp= Point2d.Minus(points[prev], points[current]);
int min = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < list.Count; j++)
{
if (!flags[list[j]])
{
if (min == -1)
{
min = list[j];
}
else
{
Point2d t = points[list[j]];
if (CompareAngel(points[min], t, points[current], dp) && GetDistance(t,points[current])<radius)
{
min = list[j];
}
}
}
}
//main.ShowMessage("seek P" + points[min].Index);
return min;
}
public int GetNextPoint_BallPivoting(int prev, int current, List<int> list, double radius)
{
SortAdjListByAngel(list, prev, current);
for (int j = 0; j < list.Count; j++)
{
if (flags[list[j]])
continue;
int adjIndex = list[j];
Point2d xianp = points[adjIndex];
Point2d rightCirleCenter = GetCircleCenter(points[current],xianp,radius);
if (!HasPointsInCircle(list,rightCirleCenter,radius,adjIndex))
{
main.DrawCircleWithXian(rightCirleCenter, points[current], points[adjIndex], radius);
return list[j];
}
}
return -1;
}
private void SortAdjListByAngel(List<int> list, int prev, int current)
{
Point2d origin = points[current];
Point2d df;
if (prev != -1)
df = new Point2d(points[prev].X - origin.X, points[prev].Y - origin.Y);
else
df = new Point2d(1, 0);
int temp = 0;
for (int i = list.Count; i > 0; i--)
{
for (int j = 0; j < i - 1; j++)
{
if (CompareAngel(points[list[j]], points[list[j + 1]], origin, df))
{
temp = list[j];
list[j] = list[j + 1];
list[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
private bool HasPointsInCircle(List<int> adjPoints,Point2d center,double radius,int adjIndex)
{
for (int k = 0; k < adjPoints.Count; k++)
{
if (adjPoints[k] != adjIndex)
{
int index2 = adjPoints[k];
if (IsInCircle(points[index2], center, radius))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static Point2d GetCircleCenter(Point2d a, Point2d b, double r)
{
double dx = b.X - a.X;
double dy = b.Y - a.Y;
double cx = 0.5 * (b.X + a.X);
double cy = 0.5 * (b.Y + a.Y);
if (r * r / (dx * dx + dy * dy) - 0.25 < 0)
{
return new Point2d(-1, -1);
}
double sqrt = Math.Sqrt(r * r / (dx * dx + dy * dy) - 0.25);
return new Point2d(cx - dy * sqrt, cy + dx * sqrt);
}
public static bool IsInCircle(Point2d p,Point2d center,double r)
{
double dis2 = (p.X - center.X) * (p.X - center.X) + (p.Y - center.Y) * (p.Y - center.Y);
return dis2 < r * r;
}
public List<int>[] GetInRNeighbourList(double radius)
{
List<int>[] adjs = new List<int>[points.Count];
for (int i = 0; i < points.Count; i++)
{
adjs[i] = new List<int>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < points.Count; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < points.Count; j++)
{
if (i < j && distanceMap[i, j] < radius)
{
adjs[i].Add(j);
adjs[j].Add(i);
}
}
}
return adjs;
}
private List<int> GetSortedNeighbours(int index)
{
List<Point2dInfo> infos = new List<Point2dInfo>(points.Count);
for (int i = 0; i < points.Count; i++)
{
infos.Add(new Point2dInfo(points[i], i, distanceMap[index, i]));
}
infos.Sort();
List<int> adj = new List<int>();
for (int i = 1; i < infos.Count; i++)
{
adj.Add(infos[i].Index);
}
return adj;
}
public static double GetDistance(Point2d p1, Point2d p2)
{
return Math.Sqrt((p1.X - p2.X) * (p1.X - p2.X) + (p1.Y - p2.Y) * (p1.Y - p2.Y));
}
public static double GetCross(Point2d a, Point2d b)
{
return a.X * b.Y - a.Y * b.X;
}
}
求解这个问题理论上还有很多思路,这些思路日后有时间还会继续在这里更新。其实笔者曾经将这个问题联系到旅行商问题和哈密顿回路。因为在有的应用场景,当人们给出一系列点,这些点来表征物体轮廓时,可能会要求所有给出的点都必须在生成的多边形上。假如有这要求的话alpha shape之类的方案就不成了,那或许就是一个旅行商问题,不过貌似旅行商问题不能保证不自交的路径,这方面笔者还没有试过,将来有时间也许会尝试一下。
算法工程下载地址:Github: https://github.com/chnhideyoshi/SeededGrow2d/tree/master/ConcaveGenerator
其实讨论这个问题的一大动机还是为了进一步探讨这一问题扩展到三维的情况,业界在这一方面也有不少成熟的研究,例如三维滚球法,PowerCrust,Cocone,假如能知道点法向,还能使用重建更加光滑局面的隐式曲面的方法如MLS,RBF,POISSON等,对三维的方法的探讨将来还会继续更新。
|
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】;
如果你在论坛求助问题,并且已经从坛友或者管理的回复中解决了问题,请把帖子标题加上【已解决】; 如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
如何回报帮助你解决问题的坛友,一个好办法就是给对方加【D豆】,加分不会扣除自己的积分,做一个热心并受欢迎的人!
 |申请友链|Archiver|手机版|小黑屋|辽公网安备|晓东CAD家园
( 辽ICP备15016793号 )
|申请友链|Archiver|手机版|小黑屋|辽公网安备|晓东CAD家园
( 辽ICP备15016793号 )